Post Login Action in Interchange
A while back, I sent a request to a few coworkers looking for a post login hook in Interchange, meaning that I’d like to execute some code after a user logs in that would not require modifying the core Interchange code. This was prompted by the need to transfer and create database records of uploaded images (uploaded while not logged in) to be tied to a specific user after they log in. Mark found a simple and elegant solution and I’ve described it below.
postlogin_action
The first step to adding a post login hook or method is to add the following to catalog.cfg:
UserDB default postlogin_action transfer_user_imagesThe above code results in a call to the catalog or global sub transfer_user_images after a user logs in.
Defining the Global Sub
Next, the sub needs to be defined. In our code, this looks like:
# custom/GlobalSub/transfer_user_images.sub
GlobalSub transfer_user_images IC::GlobalSubs::transfer_user_images# custom/lib/IC/GlobalSubs.pm
sub transfer_user_images {
#code here
}In the above example a transfer_user_images sub points to a Perl module that contains all of our custom global subroutines. The GlobalSubs Perl module contains the code executed upon login.
Add …
ecommerce interchange perl
Internal Tidbits: Links, Resources, Tools
Here at End Point, we have a broad range and depth of knowledge in many areas of web development, both server side and client side. This shows itself in form of many internal emails. Whenever I get an internal email with some tidbit of information I’d like to read later on, I file it in my Internal folder to read about later. That folder is overflowing now, and I wanted to take some time to clean it out and share the contents in blog form.
- A while back, Jon shared a link to superhero.js, which is an aggregate of the best articles, videos and presentations on creating, testing, and maintaining large JavaScript code bases.
- Jon also shared a link to Coding, Fast and Slow: Developers and the Psychology of Overconfidence. This is an article about estimating projects, which is so inherent in our work.
- Phunk told us about the file finder tool in github: if you go to a repo in github and click “t”, it activates the file finder and you can find files by fragments of the filename. Holy cow – I’m just reading this email now and tried it out for the first time!
- Jon shared a link to Git Best Practices by Seth Robertson.
- Jon (side note: This Jon “character” must send a lot of emails!) told us …
tools
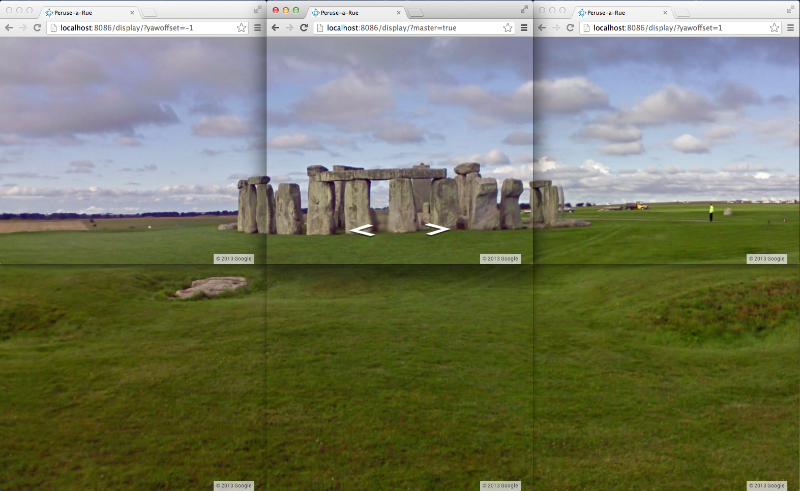
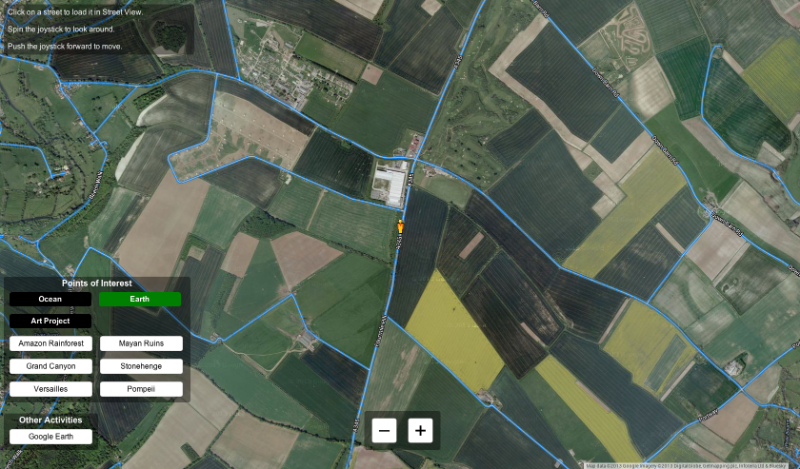
Liquid Galaxy and its Very Own Street View App
Liquid Galaxy does Street View!
Peruse-a-Rue is the combination of a Node.js server with a Maps API browser client, all wrapped up in one neat bundle. The result of this marriage is a highly compelling immersive Street View experience.
Everything from a single screen kiosk to a cylindrical Liquid Galaxy to an endless display wall can be configured, with bezel offsets, portrait or landscape. A touchscreen control interface is optional, and a Space Navigator can drive the display.
By leveraging the Connect framework for Node, the entire application is served on a single port. Any number of browser windows can be synchronized, thanks to the scalability of websockets. When integrated with the Squid caching of the Liquid Galaxy project, redundant downloading is eliminated; each screen shares retrieved tile data with its peers.
Since NPM installs dependencies automatically, deployment is a breeze. Every Liquid Galaxy is a git checkout and an npm install away from running the server. Peruse-a-Rue supports any operating system that can run Node.js (as a server) or Google Chrome (as a client). I’ve even tested the …
javascript visionport nodejs
How to Dynamically Update A Spree Product’s Price Based on Volume Pricing
I was recently working on a Spree Commerce site that utilizes Spree’s Volume Pricing extension. For those who may not be familiar, the Spree Commerce Volume Pricing extension allows a user to offer a variety of ‘price ranges’. These price ranges represent discounted prices per unit for larger quantity orders. For example (we will use this t-shirt pricing table for the remainder of the post) from the Spree Volume Pricing Github
Variant Name Range Amount Position
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Rails T-Shirt 1-5 (1..5) 19.99 1
Rails T-Shirt 6-9 (6...10) 18.99 2
Rails T-Shirt 10 or more (10+) 17.99 3I would like to mention that these ranges, although resembling traditional ranges, are expressed as Strings as this will become more important later. Again from the Spree Volume Pricing project page at Github,
“All ranges need to be expressed as Strings and must include parentheses. ‘(1..10)’ is considered to be a valid range. ‘1..10’ is not considered to be a valid range …
ecommerce javascript ruby rails spree
IE7 “Enhances” href Attributes of Links Added via innerHTML
I ran into this issue the other day while testing a new feature for a client site. The code worked well in Chrome, Firefox, Safari and IE (8-11) but it blew up in IE7. The page was fairly straightforward—I was using jQuery and the excellent doT.js templating library to build up some HTML and add it to the page after the DOM had loaded. This content included several links like so:
<a href="#panel1">More Info</a>
<a href="#panel2">More Info</a>
<a href="#panel3">More Info</a>Each of the links pointed to their corresponding counterparts which had also been added to the page. The JavaScript code in question responded to clicks on the “More Info” links and used their href attribute as a jQuery selector:
$('.my-links').on('click', function(e) {
e.preventDefault();
var sel = $(this).attr('href');
...
});
Links “Enhanced” By IE7
As I debugged in IE7, I determined that it was adding the fully qualified domain name to the links. Instead of “#panel2” the href attributes were set to “http://example.com/#panel2” which broke things—especially my jQuery selectors. Fixing …
browsers javascript jquery tips
Install Pentaho BI Server 4.8 Community Edition with PostgreSQL Repository
Pentaho BI server community edition can be installed through an archive file available from SourceForge.
Prerequisites
- Java 6
- PostgreSQL
Download Pentaho BI Server installation file (biserver-ce-4.8.0-stable.zip) from SourceForge: http://sourceforge.net/projects/pentaho/files/Business%20Intelligence%20Server/4.8.0-stable
Unzip the archive file and navigate inside biserver-ce to set sh files to executable mode:
$ unzip biserver-ce-4.8.0-stable.zip
$ cd biserver-ce
$ find . -type f -iname '*.sh' -exec chmod a+x {} \;Pentaho community edition uses hsql database as default. Need to create two databases in Postgres for Pentaho. Find the SQL files to create databases under biserver-ce/data/postgresql. database_name, user_name and password are configurable through SQL files. Fix two errors before creating database using SQL files. Comment two lines in below files tables as commented.
- create_quartz_postgresql.sql
ALTER TABLE qrtz_fired_triggers
ALTER TRIGGER_NAME TYPE VARCHAR(200),
ALTER TRIGGER_GROUP TYPE VARCHAR(200),
ALTER INSTANCE_NAME TYPE VARCHAR(200),
ALTER JOB_NAME TYPE VARCHAR(200),
ALTER JOB_GROUP TYPE VARCHAR(200),
ADD COLUMN …analytics pentaho postgres casepointer
Install Pentaho BI Server 5 Enterprise Edition with PostgreSQL repository
Pentaho provides different ways to install Pentaho BI server. Each method has its own flexibility in installation.
-
Installer mode—Easy to install BA & DI server & tools in one flow with default PostgreSQL repo & default Tomcat server. (New Postgres installed on port 5432.)
-
Archive mode—BA server installed with own BA repository & default Tomcat server. Necessary tools need to be installed manually.
-
Manual mode—BA server installed with own BA repository & own application server (Tomcat or JBoss). Necessary tools need to installed manually.
We have a Postgres instance running on our server and are good with Tomcat as application server so Archive mode of installation is suitable for us. Pentaho installation requires two things be installed before starting with Pentaho installation.
- Java 7
- PostgreSQL
Archive mode installation files can be accessible only to license purchased users. Download biserver-ee-5.x-dist.zip from Pentaho customer portal with account credentials here: https://support.pentaho.com/forums/20413716-Downloads
Unzip the archive file and you can see the installation files inside extracted directory.
$ unzip biserver-ee-5.x-dist.zip
$ cd …analytics pentaho postgres casepointer
Specify versions for your dependencies in your Gemfiles
How often have you been too lazy to put a version spec for gems you depended on in your projects? Do you fear updating the gems your app uses in production?
Here is an elusive-obvious tip for you: Always specify version numbers for your dependencies in your app’s Gemfile.
Version specs should:
-
be strict numbers for very fragile gems like Rails
-
use the pessimistic operator for others (with ~>)
Updating apps with versionless Gemfiles is painful
Newer gem versions often break compatibility. That makes updating a disaster if you don’t have any restrictions in place for your dependencies.
We should coin a new term in the field of psychology: Update Anxiety.
That’s precisely the state the vast majority of us is in when proceeding to update dependencies in our projects.
In Rails, having a versionless Gemfile makes clean updates impossible.
Fearing the update makes your app susceptible to bugs
Newer versions of gems are there, not only for delivering new features. The history of changes between different versions mostly show changes related to bug fixes. If you see a gem which mostly delivers new features without fixing bugs—stay away from it!
If you do not update the gem set out …
ruby rails