Simple AngularJS Page
The best thing in AngularJS is the great automation of actualizing the data in the HTML code.
To show how easy Angular is to use, I will create a very simple page using AngularJS and Github.
Every GitHub user can get lots of notifications. All of them can be seen at GitHub notification page. There is also the GitHub API, which can be used for getting the notification information, using simple HTTP requests, which return JSON.
I wanted to create a simple page with a list of notifications. With information if the notification was read (I used “!!!” for unread ones). And with automatical refreshing every 10 minutes.
To access the GitHub API, first I generated an application token on the GitHub token page. Then I downloaded a file from the AngularJS page, and a GitHub API JavaScript wrapper.
Then I wrote a simple HTML file:
<html>
<head>
<script src="angular.min.js"></script>
<script src="underscore-min.js"></script>
<script src="github.js"></script>
<script src="jscode.js"></script>
</head>
<body ng-app="githubChecker">
<div ng-controller= …angular javascript
Simple cross-browser communication with ROS
ROS and RobotWebTools have been extremely useful in building our latest crop of distributed interactive experiences. We’re continuing to develop browser-fronted ROS experiences very quickly based on their huge catalog of existing device drivers. Whether a customer wants their interaction to use a touchscreen, joystick, lights, sound, or just about anything you can plug into the wall, we now say with confidence: “Yeah, we can do that.”
A typical ROS system is made out of a group (“graph”) of nodes that communicate with (usually TCP) messaging. Topics for messaging can be either publish/subscribe namespaces or request/response services. ROS bindings exist for several languages, but C++ and Python are the only supported direct programming interfaces. ROS nodes can be custom logic processors, aggregators, arbitrators, command-line tools for debugging, native Arduino sketches, or just about any other imaginable consumer of the data streams from other nodes.
The rosbridge server, implemented with rospy in Python, is a ROS node that provides a web socket interface to the ROS graph with a simple JSON protocol, making it easy to communicate with ROS from any language that can connect to a …
javascript visionport ros
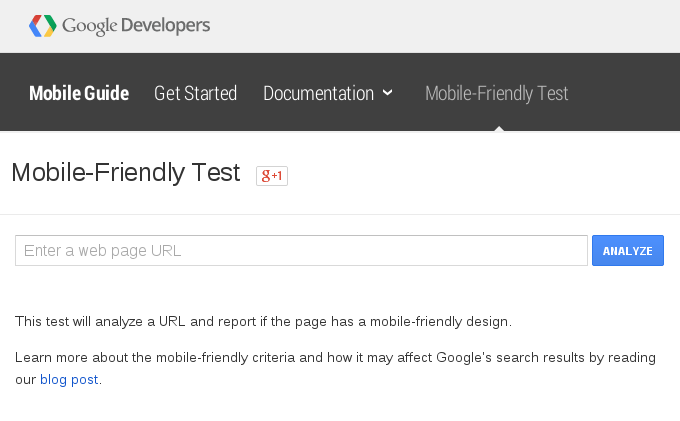
Mobile-friendly sites or bust!
A few weeks ago, Google announced that starting on April 21 it will expand its “use of mobile-friendliness as a ranking signal” which “will have a significant impact in our search results”.
The world of search engine optimization and online marketing is aflutter about this announcement, given that even subtle changes in Google’s ranking algorithm can have major effects to improve or worsen any particular site’s ranking. And the announcement was made less than two months in advance of the announced date of the change, so there is not much time to dawdle.
Google has lately been increasing its pressure on webmasters (is that still a real term‽) such as with its announcement last fall of an accelerated timetable for sunsetting SSL certificates with SHA-1 signatures. So far these accelerated changes have been a good thing for most people on the Internet.
In this case, Google provides an easy Mobile-Friendly Site Test that you can run on your sites to see if you need to make changes or not:
So get on it and check those sites! I know we have a few that we can do some work on.
design mobile search
Advanced Product Filtering in Ecommerce
One of my recent projects for Paper Source has been to introduce advanced product filtering (or faceted filtering). Paper Source runs on Interchange, a perl-based open source ecommerce platform that End Point has been involved with (as core developers & maintainers) for many years.
In the case of Paper Source, personalized products such as wedding invitations and save the dates have advanced filtering to filter by print method, number of photos, style, etc. Advanced product filtering is a very common feature in ecommerce systems with a large number of products that allows a user to narrow down a set of products to meet their needs. Advanced product filtering is not unlike faceted filtering offered by many search engines, which similarly allows a user to narrow down products based on specific tags or facets (e.g. see many Amazon filters on the left column). In the case of Paper Source, I wrote the filtering code layered on top of the current navigation. Below I’ll go through some of the details with small code examples.
Data Model
The best place to start is the data model. A simplified existing data model that represents product taxonomy might look like the following:
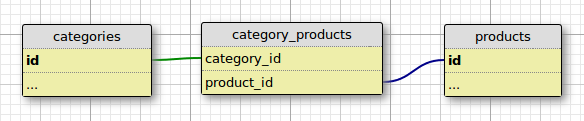
Basic …
ecommerce interchange
wroc_love.rb a.k.a. “The best Java conference in Ruby world”
Time and Date: 13–15th March 2015
Place: Wrocław University
Amongst many Ruby and Rails talks on this conference, there were some not related to Ruby at all. Since 2013 I have observed a growing number of functional programming topics and concerns. Even the open discussion was mainly devoted not to OOP but to concepts like Event Sourcing or patterns similar to those promoted by Erlang or Clojure.
So let’s enumerate the best moments.
First of all, the “ClojureScript + React.js” presented by Norbert Wójtowicz. The link below points to the presentation that was recorded on Lambda Days. It is a fascinating talk about gigantic technology leap that is going to have a impact on the whole OOP world.
Nicolas Dermine presented Overtone’s implemented mostly in Ruby that’s called Sonic Pi which lets you basically write code that plays music. It is a great tool from which to learn programming and to use to have fun in the same time. It is also a great tool for teachers (both music and programming).
Awesome project! http://t.co/c2NUNpYjwS Coding music in #ruby Thanks @nicoder for your talk #wrocloverb pic.twitter.com/sY4MpqhZlf
— Cecile Veneziani (@cecilitse) March 14, 2015
There was also a …
clojure conference erlang functional-programming javascript ruby
HTTP/2 is on the way!
HTTPS and SPDY
Back in August 2014, we made our websites www.endpoint.com and liquidgalaxy.endpoint.com HTTPS-only, which allowed us to turn on HTTP Strict Transport Security and earn a grade of A+ from Qualys’ SSL Labs server test.
Given the widely-publicized surveillance of Internet traffic and injection of advertisements and tracking beacons into plain HTTP traffic by some unscrupulous Internet providers, we felt it would be good to start using TLS encryption on even our non-confidential public websites.
This removed any problems switching between HTTP for most pages and HTTPS for the contact form and the POST of submitted data. Site delivery over HTTPS also serves as a ranking signal for Google, though presumably still a minor one.
Doesn’t SSL/TLS slow down a website? Simply put, not really these days. See Is TLS Fast Yet? for lots of details. And:
Moving to HTTPS everywhere on our sites also allowed us to take advantage of nginx’s relatively new SPDY (pronounced “speedy”) capability. SPDY is an enhancement to HTTPS created by Google to increase web page delivery time by compressing headers and multiplexing many requests in a single TCP connection. It is only available on …
networking sysadmin compression
Cross Release APT Managment aka How to Watch Netflix on Debian 7 Wheezy
Native Netflix video streaming has come to GnuLinux! …if you have the correct library versions.
I am currently running GNU-Linux Debian 7 Wheezy with OpenBox. I really enjoy this lightweight, speedy and easily customized window manager (OpenBox uses simple XML configuration files). So I was also pretty excited when Netflix added HTML5 streaming support and read that folks were proclaiming success in Google Chrome browsers without necessitating any agent masking workarounds.
However, I found I was still getting errors when attempting to stream video in Chrome. The forums I was reading were reporting that when using the Chrome 36+ browser, Netflix would allow Linux streaming. Most all of these forums were based in a Ubuntu 14.04+ environment. Nevertheless, I found a hint as to how to proceed in Debian after reading this article regarding libnss:
“Netflix streams its video in HTML5, but uses a technology called Encrypted Media Extensions to prevent piracy. These extensions in turn require a set of libraries called Network Security Services that the browser can access.”
Debian Wheezy’s repo list maxed out at libnss3==2:3.14 and I would need libnss3==2:3.16+ in order to pass …
debian html linux
On End Point’s Development Environment
A few recent conversations have sparked my interest in writing up a blog post that summarizes the familiar elements of our development environments. The majority of End Pointers work remotely, but many of the tools listed below are common to many developers.
- ssh/sftp: We do primarily remote development. Many of us are familiar with local development, but remote development with camps (see next point) is typically the most efficient arrangement in working with multiple development instances that are accessible to clients for testing and staging.
- camps: DevCamps are a tool specific to and created by End Point, which are development instances with an entire webserver, database, and app server stack, similar to containers like Docker. Check out the DevCamps website for more information.
- vim/emacs/nano: While most of our employees use vim or emacs for command-line editors, nano is an inefficient but easy to use editor that we can suggest to new developers. Not many of us use IDEs, if at all.
- screen/tmux: screen and tmux are our preferred terminal multitasking and sharing.
- command-line database interaction (specifically psql and mysql ad-hoc querying): Working with an SQL database …
company environment tools remote-work