DBD::Pg, UTF-8, and Postgres client_encoding
 Photo by Roger Smith
Photo by Roger Smith
I’ve been working on getting DBD::Pg to play nicely with UTF-8, as the current system is suboptimal at best. DBD::Pg is the Perl interface to Postgres, and is the glue code that takes the data from the database (via libpq) and gives it to your Perl program. However, not all data is created equal, and that’s where the complications begin.
Currently, everything coming back from the database is, by default, treated as byte soup, meaning no conversion is done, and no strings are marked as utf8 (Perl strings are actually objects in which one of the attributes you can set is ‘utf8’). If you want strings marked as utf8, you must currently set the pg_enable_utf8 attribute on the database handle like so:
$dbh->{pg_enable_utf8} = 1;This causes DBD::Pg to scan incoming strings for high bits and mark the string as utf8 if it finds them. There are a few drawbacks to this system:
- It does this for all databases, even SQL_ASCII!
- It doesn’t do this for everything, e.g. arrays, custom data types, xml.
- It requires the user to remember to set pg_enable_utf8.
- It adds overhead as we have to parse every single byte coming back from the database.
Here’s one proposal for a new …
database dbdpg perl postgres
SSH config wildcards and multiple Postgres servers per client
The SSH config file has some nice features that help me to keep my sanity among a wide variety of servers spread across many different clients. Nearly all of my Postgres work is done by using SSH to connect to remote client sites, so the ability to connect to the various servers easily and intuitively is important. I’ll go over an example of how a ssh config file might progress as you deal with an ever‑expanding client.
Some quick background: the ssh config file is a per‑user configuration file for the SSH program. It typically exists as ~/.ssh/config. It has two main purposes: setting global configuration items (such as ForwardX11 no), and setting things on a host‑by‑host basis. We’ll be focusing on the latter.
Inside the ssh config file, you can create Host sections which specify options that apply only to one or more matching hosts. The sections are applied if the host name you type in as the argument to the ssh command matches what is after the word “Host”. As we’ll see, this also allows for wildcards, which can be very useful.
I’m going to walk through a hypothetical client, Acme Corporation, and show how the ssh config can grow as the client does, until the final example …
clients linux postgres ssh sysadmin tips
New Year Bug Bites
Happy New Year! And what would a new year be without a new year bug bite? This year we had one where figuring out the species wasn’t easy.
On January 2nd one of our ecommerce clients reported that starting with the new year a number of customers weren’t able to complete their web orders because of credit card security code failures. Looking in the Interchange server error logs we indeed found a significant spike in the number of CVV2 code verification failures (Payflow Pro gateway error code “114”) starting January 1st.
We hadn’t made any programming or configuration changes on the system in the recent days. We double-checked to make sure: nope, no code changes. So it had to be a New Year’s bug and presumably something with the Payflow Pro gateway or banks further upstream. We checked error logs for other customers to see if they were being similarly impacted, but they weren’t. Our client contacted PayPal (the vendor for Payflow Pro) and they reported there were no problems with their system. The failures must indeed be card failures or a problem with the website according to them. We further checked our code looking for what we could possibly have done that might be the cause, …
analytics ecommerce interchange javascript
jQuery code for making a block level element clickable while maintaining left/middle/right clicking
While working on a recent redesign for a client we needed the ability to click on a div and have it function as a link to a product page. The initial implementation used the jQuery plugin BigTarget.js. The plugin searches within the div for a link and when the div is clicked changes the location to the link that is found. This plugin worked fine and was fairly easy to setup, however there was one drawback that we found once it was released in the wild. Most people expect to be able to right click, middle click, shift click, and control click to get the context-sensitive menu, open in a new window, or open in a new tab.
Enter Superlink.js, a jQuery plugin that uses a cool trick of moving the location of a link to the location of the mouse within the block level element (such as a div, li, tr, td, etc.). With this implementation the mouse is actually over a link so that the various ways of clicking function as expected. Initially I started moving the clickable area within a table, as shown in the example, but then quickly realized there was no reason this shouldn’t work within a div or li. One other neat thing with this plugin is that the events attached to the block will continue to …
javascript jquery tips
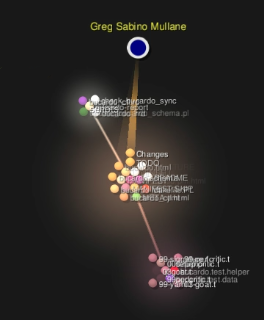
Version Control Visualization and End Point in Open Source
Over the weekend, I discovered an open source tool for version control visualization, Gource. I decided to put together a few videos to showcase End Point’s involvement in several open source projects.
Here’s a quick legend to help understand the videos below:
The Videos
Interchange from endpoint on Vimeo.
Bucardo from endpoint on Vimeo.
One of the articles that references Gource suggests that the videos can be used to visualize and analyze the community involvement of a project (open source or not). One might also be able to qualitatively analyze the stability of project file architecture …
git interchange postgres spree open-source
Character encoding in perl: decode_utf8() vs decode('utf8')
When doing some recent encoding-based work in Perl, I found myself in a situation which seemed fairly unexplainable. I had a function which used some data which was encoded as UTF-8, ran Encode::decode_utf8() on said data to convert to Perl’s internal character format, then converted the “wide” characters to the numeric entity using HTML::Entities::encode_entities_numeric(). Logging/printing of the data on input confirmed that the data was properly formatted UTF-8, as did running iconv -f utf8 -t utf8 output.log >/dev/null for the purposes of review.
However when I ended up processing the data, it was as if I had not run the decode function at all. In this case, the character in question was € (unicode code point U+20AC). The expected behavior from encode_entities_numeric() would be to turn any of the hi-bit characters in the perl string (i.e. all Unicode code points > 0x80) into the corresponding numeric entity (€ - € in this case). However instead of that specific character’s numeric entity appearing in the output, the entities which appeared were: ⬠i.e., the raw UTF-8 encoded value for €, with each octet being treated as an independent character instead of part of the …
database interchange perl
SearchToolbar and dropped Interchange sessions
A new update to Interchange’s robots.cfg can be found here. This update adds “SearchToolbar” to the NotRobotUA directive which is used to exclude certain user agent strings when determining whether an incoming request is from a search engine robot or not. The SearchToolbar addon for IE and FireFox is being used more widely and we have received reports that users of this addon are unable to add items to their cart, checkout, etc. You may remember a similiar issue with the Ask.com toolbar that we discussed in this post. If you are using Interchange you should download the latest robots.cfg and restart Interchange.
ecommerce interchange
Using “diff” and “git” to locate original revision/source of externally modified files
I recently ran into an issue where I had a source file of unknown version which had been substantially modified from its original form, and I wanted to find the version of the originating software that it had originally come from to compare the changes. This file could have come from any number of the 100 tagged releases in the repository, so obviously a hand-review approach was out of the question. While there were certainly clues in the source file (i.e., copyright dates to narrow down the range of commits to review) I thought up and used this technique:
Here are our considerations:
- We know that the number of changes to the original file is likely small compared to the size of the file overall.
- Since we’re trying to uncover a likely match for the purposes of reviewing, exactness is not required; i.e., if there are lines in common with future releases, we’re interested in the changes, so a revision with the fewest number of changes is preferred over finding the exact version of the file that this was originally based on.
The basic thought, then, is that we want to take the content of the unversioned file (i.e., the file that was changed) and find the revision of the …
development git