Postgres SQL Backup Gzip Shrinkage, aka Don’t Panic!!!
I was investigating a recent Postgres server issue, where we had discovered that one of the RAM modules on the server in question had gone bad. Unsurprisingly, one of the things we looked at was the possibility of having to do a restore from a SQL dump, as if there had been any potential corruption to the data directory, a base backup would potentially have been subject to the same possible errors that we were trying to restore to avoid.
As it was already the middle of the night (anyone have a server emergency during the normal business hours?), my investigations were hampered by my lack of sleep.
If there had been some data directory corruption, the pg_dump process would likely fail earlier than in the backup process, and we’d expect the dumps to be truncated; ideally this wasn’t the case, as memory testing had not shown the DIMM to be bad, but the sensor had alerted us as well.
I logged into the backup server and looked at the backup dumps; from the alerts that we’d gotten, the memory was flagged bad on January 3. I listed the files, and noticed the following oddity:
-rw-r--r-- 1 postgres postgres 2379274138 Jan 1 04:33 backup-Jan-01.sql.gz
-rw-r--r-- 1 postgres postgres …database postgres tips compression
DevCamps on different systems, including Plesk, CPanel and ISPConfig
In the last few months I’ve been active setting up DevCamps for several of our newer clients. DevCamps is an open source development environment system, that once setup, allows for easily starting up and tearing down a development environment for a specific site/code base.
I’ve done many camps setups, and you tend to run into surprises from system to system, but what was most interesting and challenging about these latest installs was that they were to be done on systems running Plesk, CPanel, and ISPConfig. Some things that are different between a normal deployment and one on the above mentioned platforms are:
-
On the Plesk system there was a secured Linux called ‘Atomic Secured Linux’ which includes the grsecurity module. One restriction of this module is (TPE) Trusted Path Execution which required the camp bin scripts to be owned by root and the bin directory could not be writable by other groups, otherwise they would fail to run.
-
Permissions are a mixed bag, where typically we set all of the files to be owned by the site owner, in Plesk there are special groups such as psacln that the files need to be owned by.
-
On the CPanel system we needed to move the admin images for …
camps hosting interchange testing
SSHFS and ServerAliveInterval
If you’re using SSHFS (as I do recently since OpenVPN started crashing frequently on my OpenBSD firewall), note that the ServerAliveInterval option for SSH can have significant impact on the stability of your mounts.
I set it to 10 seconds on my system and have been happy with the results so far. It could probably safely go considerably higher than that.
It’s not on by default, which leaves the stability of your SSH tunnels up to the success of TCP keepalive (which is on by default). On my wireless network, that alone has not been sufficient.
hosting security tips
Common Topics in Scalability
It rarely makes sense for a startup business to tackle scalability questions from the outset, because it raises the cost and complexity of development and operational support, while solving problems that a start-up business doesn’t typically yet need solved (i.e. handling tons of users). From a cost-effectiveness perspective, it makes sense to solve these problems when the need is actually evident.
That said, systems can be designed with scalability in mind such that the system easily lends itself to incremental changes that scale up its capacity.
The basic principles and techniques that typically come up in scalability discussions:
-
horizontal scalability: a particular component is “horizontally scalable” if you can deploy redundant instances of that component in parallel; this is the ultimate scalability win, as it means you can readily add raw processing power for that component at low cost.
-
vertical scalability: the practice of increasing a single component’s power/capacity to improve performance/throughput is referred to as “vertically scaling” that component. From the layperson’s perspective, this is the most easily-understood technique, as it effectively amounts to buying …
scalability
End Point Blogging Stats Year In Review
Many of the blogs I follow recently published a list of most popular articles from 2009, so I thought we should too. End Point started the blog in July of 2008, and has since then backported our older technical articles and company news to the blog, which is why you may see older articles in the archives. In 2009, we published just over 150 articles.
Here’s a breakdown of article categories (the categorization was a bit difficult: the “Tips, Community, Etc.” was a fallback category for any articles that didn’t have more than a few similar articles):
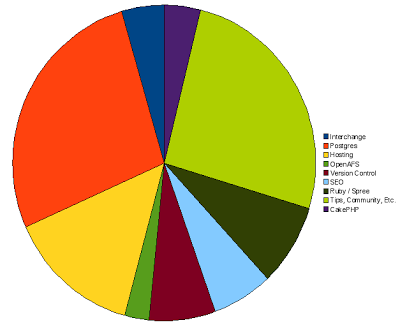
In 2009, the top 10 articles with the highest number of unique visitors were:
- /blog/2008/07/git-push-know-your-refspecs
- /blog/2008/11/10000-databases-on-postgresql-cluster
- /blog/2009/02/slony1-200-postgresql-84devel
- /blog/2009/01/slow-xen-virtualization-of-rhel-3-i386
- /blog/2009/08/file-test-comparison-table-for-shell
- /blog/2009/12/mysql-and-postgres-command-equivalents
- /blog/2008/08/switching-from-sendmail-to-postfix-on
- /blog/2008/11/multiple-reverse-dns-pointers-per-ip
- /blog/2008/08/acts-as-xapian-it-just-works
- /blog/2008/12/truecrypte-whole-disk-encryption-for
The top 10 “Top Pages”, according to a tool provided by SEOmoz, which …
analytics company
State of the Postgres project
It’s been interesting watching the MySQL drama unfold, but I have to take issue when people start trying to drag Postgres into it again by spreading FUD (Fear, Uncertainty, and Doubt). Rather than simply rebut the FUD, I thought this was a good opportunity to examine the strength of the Postgres project.
Monty recently espoused the following in a blog comment:
“…This case is about ensuring that Oracle doesn’t gain money and market share by killing an Open Source competitor. Today MySQL, tomorrow PostgreSQL.
Yes, PostgreSQL can also be killed; To prove the case, think what would happen if someone managed to ensure that the top 20 core PostgreSQL developers could not develop PostgreSQL anymore or if each of these developers would fork their own PostgreSQL project.”
Later on in his blog he raises the same theme again with a slight bit more detail:
“Note that not even PostgreSQL is safe from this threat! For example, Oracle could buy some companies developing PostgreSQL and target the core developers. Without the core developers working actively on PostgreSQL, the PostgreSQL project will be weakened tremendously and it could even die as a result.”
Is this a valid concern? It’s …
community database mysql postgres
Monitoring Postgres log files with tail_n_mail
We’ve just publically released a useful script named tail_n_mail that keeps an eye on your Postgres log files and mails interesting lines to one or more addresses. It’s released under a BSD license and is available at:
https://bucardo.org/tail_n_mail/
Complete documentation is available at the above, but here’s a quick overview. First, it figures out the current log file (it actually works for any file, but it’s primarily aimed at Postgres log files). Then, it finds any lines that match based on the INCLUDE lines in the config file, and finally removes any that do not match the EXCLUDE lines in the config files. It summarizes the results and sends a report to one or more emails.
To use, just specify a a configuration file as the first argument. Typically, the script is run from cron, either for instant reports (e.g. FATAL or PANIC errors), or for daily reports (e.g. all interesting ERRORs in the last 24 hours).
Here’s what a typical config file looks like. In this example, we’ll look for any FATAL or PANIC notices from Postgres, while ignoring a few known errors that we don’t care about.
## Config file for the tail_n_mail.pl program
## This file is automatically updated
EMAIL: …database monitoring open-source perl postgres
JPEG compression: quality or quantity?
There are many aspects of JPEG files that are interesting to web site developers, such as:
- The optimal trade off between quality and file size for any encoder and uncompressed source image.
- Reducing size of an existing JPEG image when the uncompressed source is unavailable, but still finding the same optimal trade-off.
- Comparison of different encoders and/or settings for quality at a given file size.
Two essential factors are file size and image quality. Bytes are objectively measurable, but image quality is much more nebulous. What to one person is a perfectly acceptable image is to another a grotesque abomination of artifacts. So the quality factor is subjective. For example, Steph sent me some images to compare compression artifacts. Here is the first one with three different settings in ImageMagick: 95, 50, and 8:
 |
 |
 |
Compare the subtle (or otherwise) differences in the following images (mouseover shows the filesize and compression setting):
 |
 |
 |
 |
Mouseover each image for the file size and ImageMagick compression setting. Additional comparisons are below. Each image can be opened in a separate browser tab for easy A/B comparison. I think many would find the setting of 8 …
browsers graphics optimization compression





