CanCan and RailsAdmin in Ecommerce
I’ve written about Rails Admin a lot lately. One thing I haven’t written about is how it can leverage CanCan for user authorization. Once a user is authenticated via Devise, CanCan adds an additional layer for you to control how users can access and interact with data from the admin.
A Simple Example
CanCan requires that you create an Ability class where all user permissions are defined. A very basic example in RailsAdmin ecommerce context might look like this:
class Ability
include CanCan::Ability
if user && user.is_admin?
can :access, :rails_admin
can :dashboard
can :manage, [User,
Product,
Order]
end
end
Note that in the above code, a user that is admin (where is_admin? returns a truthy reponse) has access to RailsAdmin, and the admin user can manage (create, read, update, destroy) all users, products, and orders.
Multi-Merchant Solution
Let’s go a little deeper. Multi-merchant solutions are a frequent request in ecommerce. Let’s say we have the following over-simplified data model, where users own and manage products and products are displayed by category:
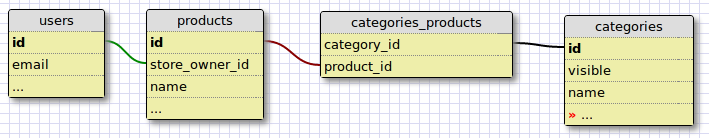
The Ability class might look like:
class Ability
include CanCan::Ability
if user && user.is_store_owner?
can :access, :rails_admin
can :dashboard
can :manage, Product, :store_owner_id => user.id
can :read, Category, :visible => true
end
if user && user.is_admin?
can :access, :rails_admin
can :dashboard
can :manage, [User,
Category,
Product,
Order]
end
end
With the above Ability definition, nothing changes for an admin user. A store owner can create products and manage (read, update, destroy) those same products. A store owner can also read categories where the category visible attribute is true. As you can see, conditions can be passed in for ability definitions. Directly from the CanCan documentation: “Anything that you can pass to a hash of conditions in Active Record will work here. The only exception is working with model ids. You can’t pass in the model objects directly, you must pass in the ids.”
Custom Abilities
In addition to the CRUD methods (create, read, update, destroy), CanCan gives you the ability to define additional custom abilities. RailsAdmin has special abilities (:history, :show_in_app, :dashboard), but you can create custom actions with RailsAdmin where CanCan abilities can be managed. For example, Marina wrote about how you might create a custom task to approve reviews here. And I described how to create a custom action to import data here, where CanCan is used to define which models can be imported and which users can do the import.
Conclusion
CanCan is decoupled from authentication and the notion of roles, which yields quite a bit of flexibility in its use. Combine RailsAdmin, CanCan, Devise, and our mountable ecommerce Rails Engine, and you’ve got a powerful set of tools for development of a custom Ruby on Rails ecommerce application with a powerful admin interface, flexible user authorization and authentication, and an extensible ecommerce solution.

Comments