Interchange Compression for SessionDB

New support for compression of sessions and more lists stored in a RDBMS has been added to core Interchange.1,2
A new module, Vend::Util::Compress, operates as a general interface for compressing and uncompressing scalar data in Interchange. The module currently offers hooks for the following compression algorithms:
- Zstd (preferred)
- Gzip
- Brotli
Additional algorithms can be easily added as needed.
Each algorithm depends on the developer having installed the necessary CPAN modules for the given compression type:
IO::Compress::Zstd/IO::Uncompress::UnZstd3IO::Compress::Gzip/IO::Uncompress::Gunzip4IO::Compress::Brotli/IO::Uncompress::Brotli5
Vend::Util::Compress exports compress() and uncompress() on demand. In scalar context, they return the reference to the scalar holding the transformed data. In list context, they return additional measurements from the process.
List compress() returns an array of:
$ref$before_size$after_size$elapsed_time$alert
List uncompress() returns an array of:
$ref$elapsed_time$alert
Any errors encountered when called in scalar context are written to the catalog error log. Errors encountered when called in list context are returned in $alert.
Compression Performance Comparison
The following chart summarizes the results of running the same Interchange instance through several steps of session growth to measure performance and impact of the three supported compression algorithms. Tests ranged from a minimum session size of 68 kilobytes up to a maximum of 110 megabytes. Fields marked in green indicate the best performance of the particular parameter, across all algorithms, for each given session size. Any fields marked in yellow indicate performance measurements reaching a level of concern. Any fields marked in red indicate measurements reaching a level of unacceptable performance in any typical situation.
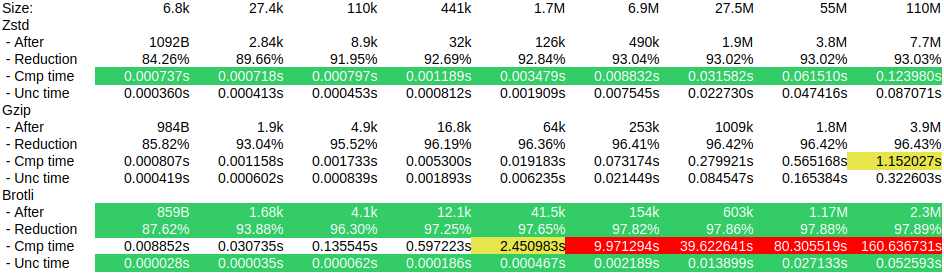
For size reduction, all 3 algorithms produced a substantial decrease across the board, generally exceeding 90% and increasing the reduction factor as the session grew. All 3 algorithms also uncompressed the session on retrieval at comparable rates, well within tolerance. Where we see significant separation is in the time to compress. Zstd is the fastest across the board, but really stands out when working with larger sessions, when the impact of compression is most needed for reducing transfer latency between the Interchange and database servers.
Configuring Your Catalog to Use Vend::Util::Compress
To begin using session compression, add the new catalog configuration parameter, SessionDBCompression, set to one of the aforementioned compression algorithms. Note the values for specifying compression type to use are case-sensitive. For example, to enable Zstd:
SessionDBCompression ZstdAn empty value for the parameter bypasses compression. An invalid value logs an error and passes through the data unmodified. If the catalog is configured for file-based sessions, the setting has no impact.
The same compression applies to both sessions and more lists when MoreDB is also set.
References
-
https://github.com/interchange/interchange/commit/35c3452bdfa1a192238196c98d12519cf153af1b ↩︎
-
https://metacpan.org/pod/IO::Compress::Zstd, https://metacpan.org/pod/IO::Uncompress::UnZstd ↩︎
-
https://metacpan.org/pod/IO::Compress::Gzip, https://metacpan.org/pod/IO::Uncompress::Gunzip ↩︎
-
https://metacpan.org/pod/IO::Compress::Brotli, https://metacpan.org/pod/IO::Uncompress::Brotli ↩︎

Comments